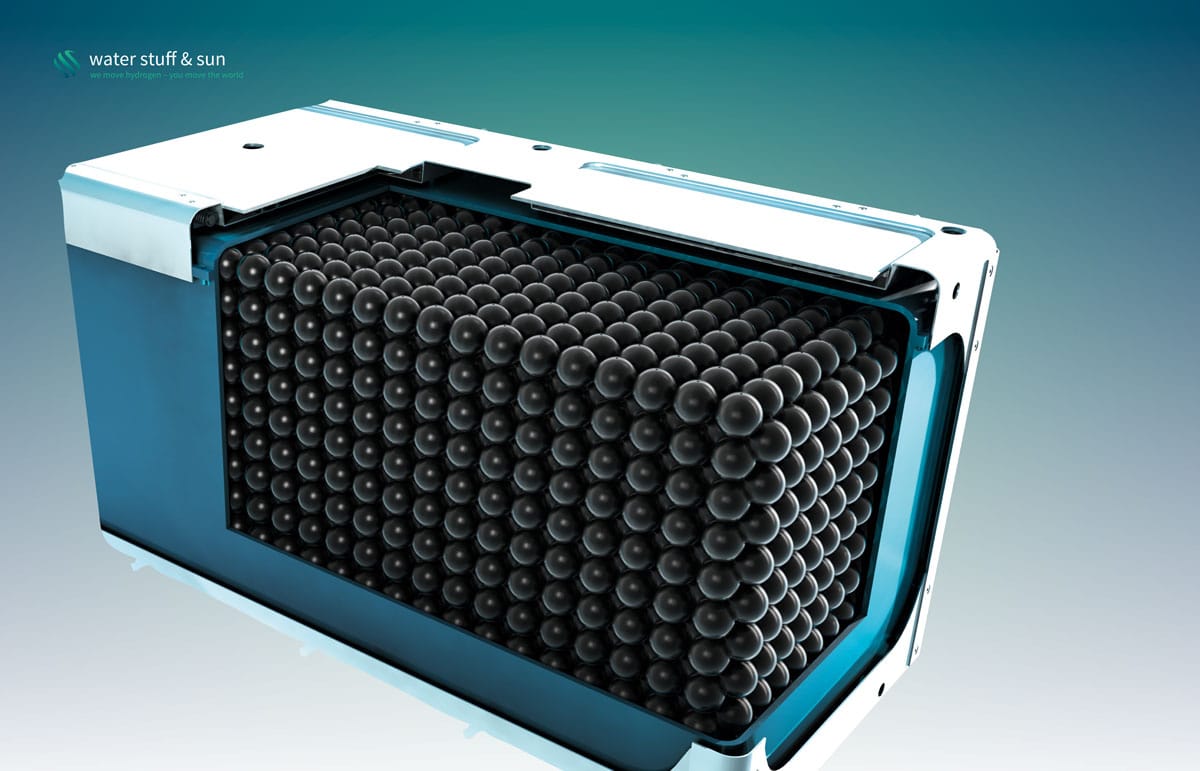
In late April, Asahi Kasei Europe started up one of its alkaline electrolyzers (see image) at the German h2herten Hydrogen Center of Excellence in Herten. The recently established business is part of the Asahi Kasei Group, a Japanese chemical company that employs 30,000 and has intimate knowledge of chloralkaline electrolysis. The electrolyzer in Herten was designed specifically to produce hydrogen from intermittent renewable sources. The initial plan is to have the system put to the test during a one-year demonstration project, co-funded by North Rhine-Westphalia’s state economic development program NRW.Invest and NRW Japan K.K. and coordinated by EnergieAgentur.NRW.
“Europe’s energy market has been witnessing dramatic changes. There is burgeoning demand for all kinds of renewable production and storage technologies,” said Hideki Tsutsumi, the president of Asahi Kasei Europe. Consequently, Asahi Kasei has been participating in other projects, such as the European Union’s three-year ALIGN-CCUS.























Very interesting, we are producing H2 by ethanol steam reforming in Mexico, but it could be the methane will be the principal fuel in the future.
Best regards