According to official statistics, waste management in Germany comprises the entire recycling economy. It differentiates between waste generation, further use and recycling as well as waste disposal. The legal basis is the Recycling Economy Act (KrWG), which is geared towards waste avoidance and recycling with the aim of protecting the environment.
The five-level waste hierarchy of the legislator (waste avoidance, preparation for re-use, recycling, other recycling and disposal) makes it clear that function-preserving re-use of products is a desirable option and contributes to sustainable added value.
Product recycling by remanufacturing, which has been known for a long time and has often been very successfully practised, is currently not included in the official statistics of the recycling economy, as this added value can be attributed to the areas of the manufacturing sector by maintaining its value. It is obvious that product recycling can be attributed to waste avoidance and is therefore at the highest level of the waste hierarchy. The allocation of remanufacturing to the manufacturing industry makes it considerably more difficult to assess its significance.
However, the remanufacturing of suitable, often high-quality products is highly lucrative as an ecological and, at the same time, economically sensible alternative to the value-destroying product disposal of the substance-based recycling economy. Accordingly, remanufacturing is a significant sales factor for many industries, such as for automotive or medical technology. [ROS]
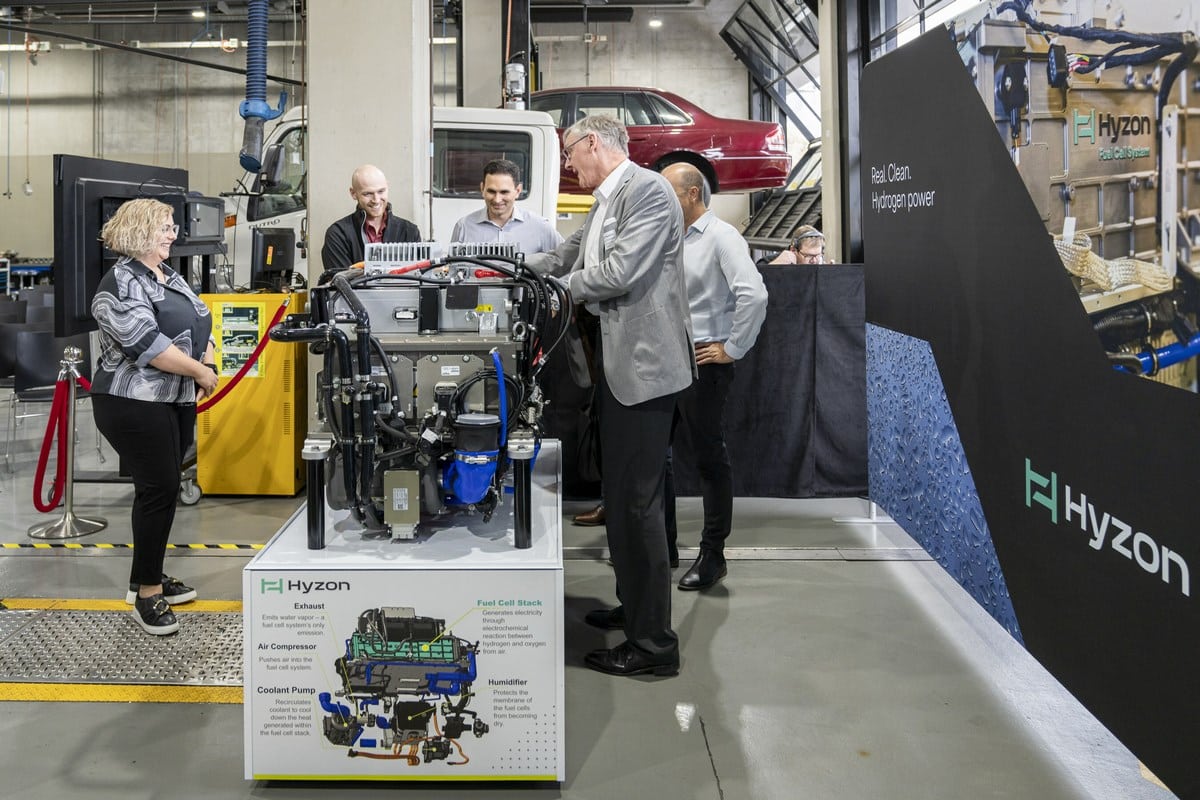
Remanufacturing of PEMFC
In order to achieve added value through remanufacturing and new marketing of quality-assured products, a number of product-dependent individual processes must be carried out, depending on the product and the objective. This includes the collection of used products – so-called cores -, incoming inspection and dismantling, detailed analysis and inspection and cleaning, remanufacturing (functional and optical/cosmetic), replacement of components if necessary, reassembly, as well as test/final inspection/warranty. [STE] The pioneer in the successful implementation of corresponding industrial processes and the establishment of lucrative markets is certainly large industry. However, small and medium-sized enterprises in particular, as drivers of innovation, can expect great opportunities in the relevant business fields. The advantages of such a strategy are concrete: Multiple benefits through multiple use [STE] – that means profitable business -, opening up new markets with high customer loyalty and satisfaction as well as sustainable and responsible entrepreneurial action.
…
read more in H2-international February 2020
Authors:
Andreas Jugenheimer
Dr. Bernd Rosemann
Prof. Frank Döpper
Caroline Hellmich
Theresa Lehmann
all University of Bayreuth






















0 Comments